Services
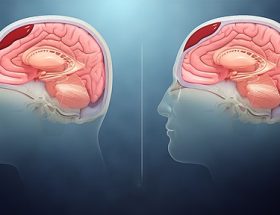
Brain Tumor
A brain tumor is a medical condition in which abnormal cells grow uncontrollably in the brain. The abnormal cells may cause damage and other problems related to the structure and function of the brain.
They occur anywhere within the central nervous system, but unlike “benign” tumors, which grow slowly, malignant tumors tend to increase over a short period.
Brain tumors are categorized based on their size and location; they’re usually divided into primary brain tumors and secondary brain tumors (metastatic).
Risk Factors
People who have had previous radiation exposure to their heads and those diagnosed with specific genetic syndromes may have an increased risk of developing a brain tumor. Additionally, there is more than one possible cause for generating a fast-growing type of cancerous brain tumor. It’s hard to identify these types of tumors until they have begun increasing and putting pressure on surrounding areas in the skull. Below are some of the significant risk factors.
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), or Lou Gehrig’s disease
- Exposure to certain chemicals
- Catastrophic seizures
- Family genetics
Symptoms to Watch Out for
Some patients with a brain tumor will have one symptom different from all of the above but can still be attributed to cancer. When you detect a significant change in your health, particularly if headaches accompany it, it’s critical to seek medical advice. Some patients with tumors will present no symptoms whatsoever.
Some of the symptoms of a brain tumor include:
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Nausea and vomiting
- Sleeping problems
- Unusual behavior or personality changes, memory loss
- Weakness in the arms and legs
- Slurred speech or difficulty speaking
- Confusion, trouble paying attention
- Hearing loss
Probable Treatments
In most cases, no immediate treatment may be necessary for a benign brain tumor because it does not grow or cause any problems. A cancerous brain tumor will often require surgical removal and possibly radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or other treatment options.
Sometimes, doctors may attempt to use more conservative treatments before attempting surgery or other more invasive procedures to shrink the tumor size. If the tumor has become too large to remove with surgery, other more aggressive and invasive treatments may be necessary, such as radiation therapy.