Services
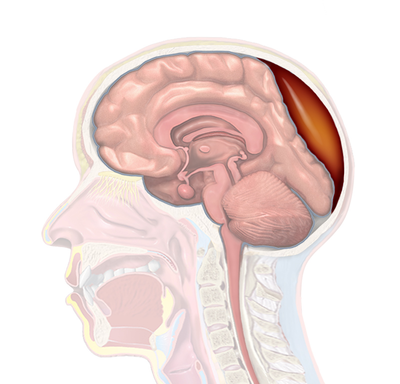
Extradural Hematoma
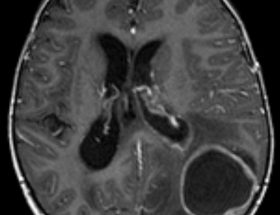
The outermost layer between the brain and skull is called the dura mater. It is the central part affected by EDH, known as Extradural Hematoma. Extradural Hematoma is a collection of blood between the skull and dura mater, the thick membrane covering your brain. The common issues faced in this disease are:
- Tear in the blood, usually in the vein and sometimes in an artery
- Blood leaking into dura mater
- The collected blood makes bubbles, and the bubbles pressure the brain, which causes brain injury
Common Symptoms of Extradural Hematoma
It is essential to understand all the symptoms of a particular disease to avoid risks and injury. If a person has Extradural Hematoma, then you can identify it by noticing some expected behaviour or pain like
- Experience in a brief loss of consciousness after head trauma
- The brain function starts declining after some hours of injury
- After some hours and minutes of damage, the person will feel severe headaches, Nausea and vomiting.
Note: The most common symptom you can notice will be in the eyes of an injured person, an enlarged pupil in one eye and the black area of the eye suddenly becoming large.
Some other symptoms you can notice are,
- Confusion
- Dizziness
- Weakness in one side of the body
- Slurred Speech
- Problem in breathing
- Coma
- Death
- Loss of brain Function
Treatment and Tests for Extradural Hematoma
Extradural Hematoma is a harmful disease, and we have to know some treatments and tests to identify and recover from this deadly disease. There are two main tests for the identification of Extradural hematoma disease,
- CT (Computed Tomography) Scan of the head and spine
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
It is a medical issue that requires emergency treatment. If a person avoids the common symptoms, the consequences can be fatal.
Surgery
Craniotomy and hematoma evacuation are the surgery part that removes the skull’s blood clot. The second one is the drilling in the skull bone, and the surgeon does drilling in the skull bone and then remove the blood clot from that particular area.